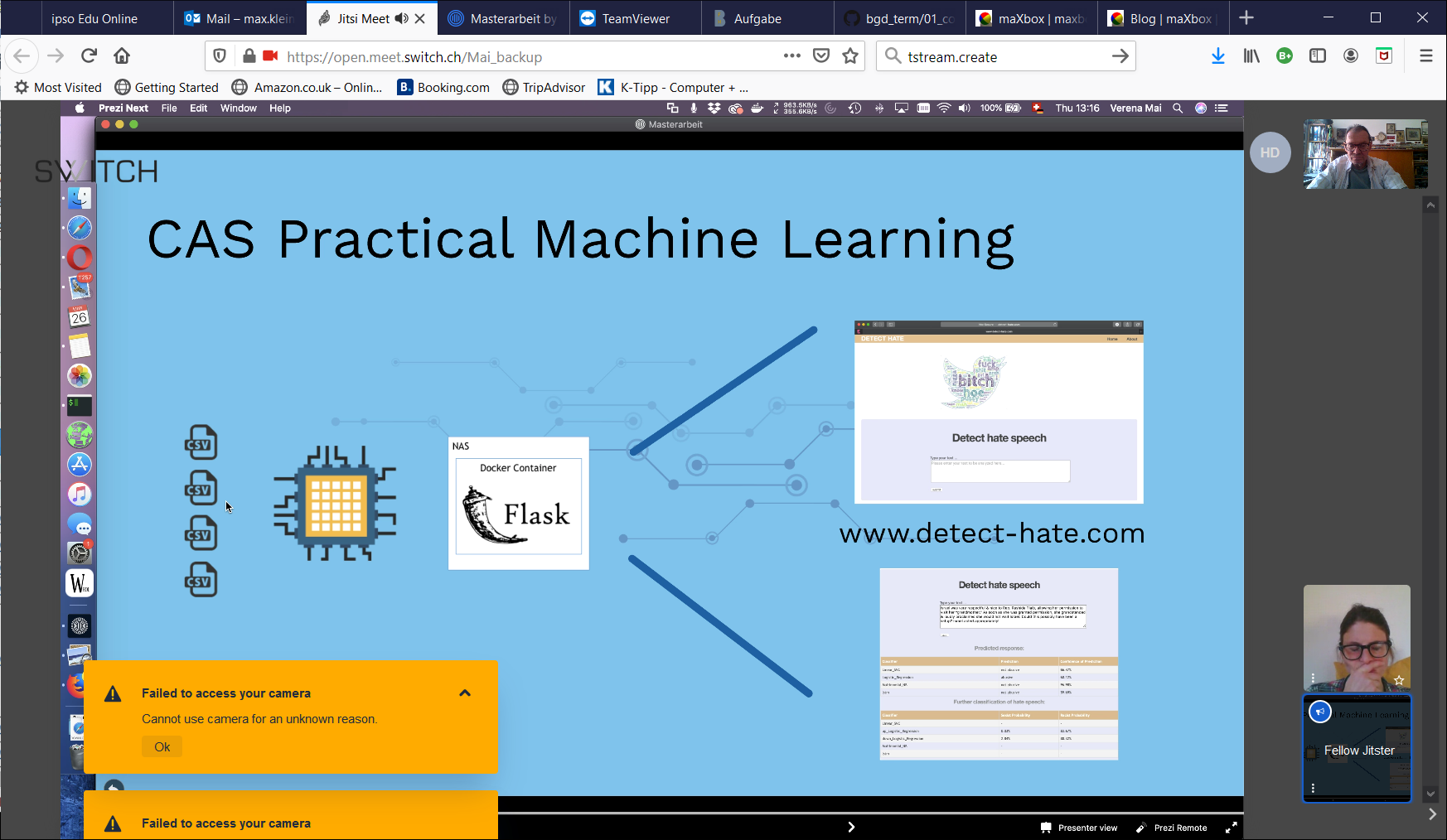
Hyperautomation is the combination of multiple machine learning (ML), packaged software and automation tools to deliver work. Hyperautomation refers not only to the breadth of the pallet of tools, but also to all the steps of automation itself (discover, analyze, design, automate, measure, monitor and reassess). Understanding the range of automation mechanisms, how they relate to one another and how they can be combined and coordinated is a major focus for hyperautomation.

A Secret is an object that contains a small amount of sensitive data such as a password, a token, or a key. Such information might otherwise be put in a Pod specification or in an image; putting it in a Secret object allows for more control over how it is used, and reduces the risk of accidental exposure.

http://www.softwareschule.ch/examples/singlesamplepredict.htm
Research: A regular expression can describe any “regular” language. These languages are ones where complexity is finite: there is a limited number of possibilities.
Caution: Some languages, like HTML, are not regular languages. This means you cannot fully parse them with traditional regular expressions.
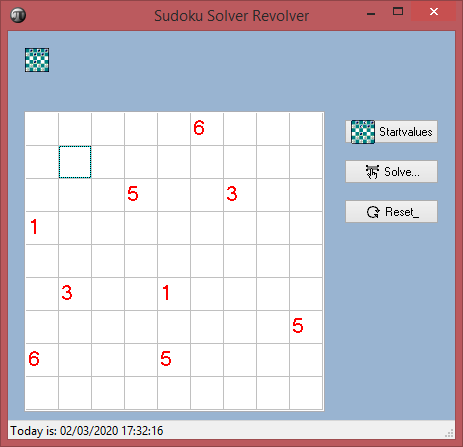
Automaton: A regular expression is based on finite state machines. These automata encode states and possible transitions to new states.
Operators: Regular expressions use compiler theory. With a compiler, we transform regular languages (like Regex) into tiny programs that mess with text.
Most classification algorithms will only perform optimally when the number of samples of each class is roughly the same. Highly skewed datasets, where the minority is heavily outnumbered by one or more classes, have proven to be a challenge while at the same time becoming more and more common.